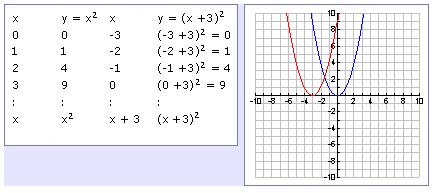
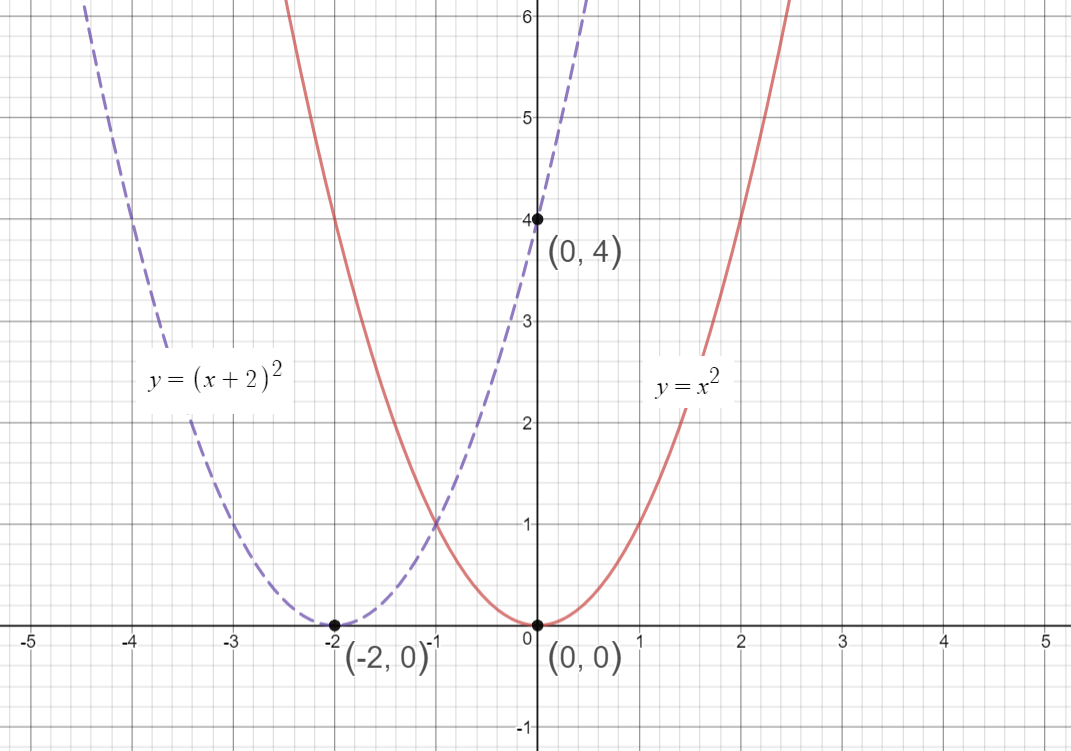
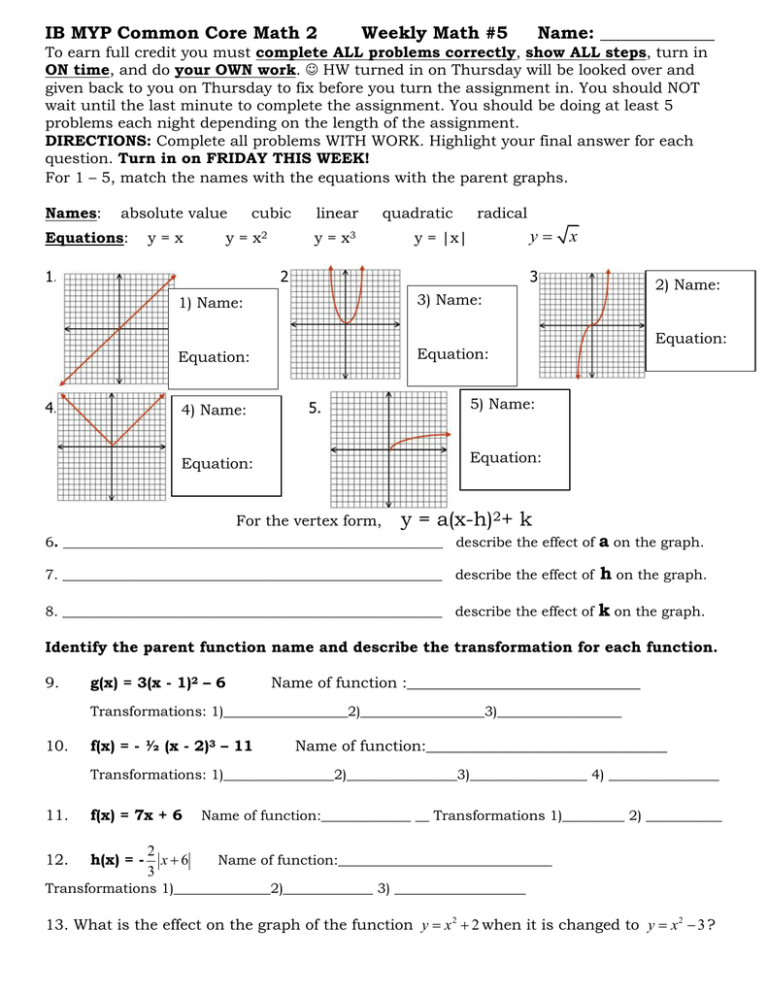
y=x^2 graph{x^2 10, 10, 5, 5} y=(x color(red)(3))^2 The graph shifts 3 units to the left graph{(x3)^2 10, 10, 5, 5} y=color(red)()(x3)^2 The graph is reflected over the xaxis graph{(x3)^2 10, 10, 5, 5} y=(x3)^2 color(red)(2) The graph is shifted 2 units down graph{(x3)^22 10, 10, 7, 3}\(y = (x a)^2\) represents a translation parallel to the \(x\)axis of the graph of \(y = x^2\) If \(a\) is positive then the graph will translate to the left If the value of \(a\) is negativeTransformations Parent or Common Functions Identity y = x Absolute Value y = x Quadratic y = x2 Each of these functions above can have transformations applied to them A transformation is an alteration to a parent function's graph There are three types of transformations translations, reflections, and dilations When a function has a

Content Transformations Of The Parabola
Y=a(x-h)^2+k transformations
Y=a(x-h)^2+k transformations-That is, the graph moves away from xaxis or towards xaxisUsing the definition of f (x), we can write y 1 (x) as,



Unit 1 6
The composite S ∘ T is a lineawr transformation S ∘ T ( x) = S ( T ( x y)) = S ( 2 x y 0) = 2 x y 0 = T ( x) Therefore, S ∘ T = T Since T is a linear transformation, we can immediately conclude that S ∘ T is a linear transformation HenceWe need an m x n matrix A to allow a linear transformation from Rn to Rm through Ax = b In the example, T R2 > R2 Hence, a 2 x 2 matrix is needed If we just used a 1 x 2 matrix A = 1 2, the transformation Ax would give us vectors in R1Describe the Transformation y=1/(x^2) The parent function is the simplest form of the type of function given For a better explanation, assume that is and is
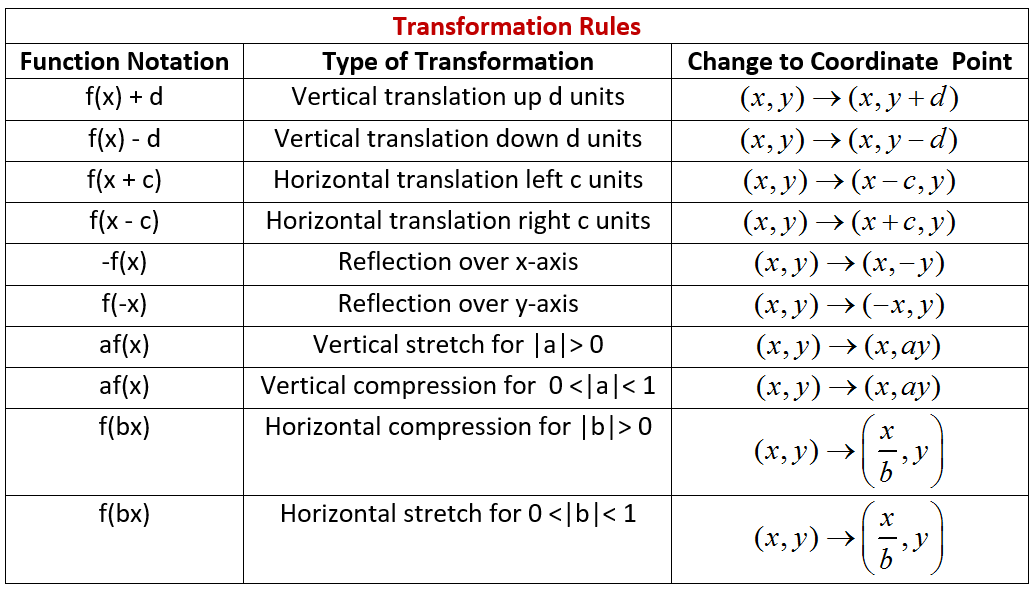
Keeping in mind that y = f ( x ), we can write this formula as ( x, f ( x )) → ( x, f (x) ) Translations of Functions f (x) k and f (x k) Translation vertically (upward or downward) f (x) k translates f (x) up or down Changes occur "outside" the function (affecting the yvalues)Definition A linear transformation is a transformation T R n → R m satisfying T ( u v )= T ( u ) T ( v ) T ( cu )= cT ( u ) for all vectors u , v in R n and all scalars c Let T R n → R m be a matrix transformation T ( x )= Ax for an m × n matrix A By this proposition in Section 23, we haveWhen deciding whether the order of the transformations matters, it helps to think about whether a transformation affects the graph vertically (ie changes the yvalues) or horizontally (ie changes the xvalues)
This video explains how to determine the equation of an expoential function with a horizontal reflection and a vertical shifthttp//mathispower4ucomStart studying Transformation Rules (x,y)> Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsAnswer choices a reflection across the line x = 4 a reflection across the line y = 4 a translation shifting f (x) 4 units to the left a translation shifting f (x) 4 units to the right




1 07 Transformations Of Functions



Transformations Of Functions Explanation Examples
Using the transformation T (x, y) (x 2, y 1), find the distance named Find the distance AB sqrt 10 Find the distance A'B' sqrt 10 Find the distance AA' sqrt 5 Find the distance BB' sqrt 5 Find the distance CC' sqrt 5 Which of the following statements isA function transformation takes whatever is the basic function f (x) and then "transforms" it (or "translates" it), which is a fancy way of saying that you change the formula a bit and thereby move the graph around For instance, the graph for y = x 2 3 looks like this Using the transformation T (x, y) (x 2, y 1), find the distance named Find the distance A'B' (I need help knowing how to work it not just the answer) 2 See answers calculista calculista we know that the rule of the translation is that means the translation is units to the right and unit up Let



Investigating Transformations Of Quadratic Graphs International Baccalaureate Maths Marked By Teachers Com




Transformations Of Section Functions 2 7 2 Learn
The graph of y=(x2)^22 is graph{(x2)^22 10, 10, 5, 5} Its transformation is a reflection over the xaxis, a translation of 2 units left and a translation of 2 units down Have a look at the following summary for transformation rules of graphs Transformations are called transformations because they start off with the "original" or "standard" function f(x) and then move/transform profile galactiicdoom2 Answer Sketch the graph of y=7^x Reflect the graph across the yaxis to show the function y=7^x Stretch the graph vertically by a factor of 3 to show the function y=3*7^x Shift the graph up 2 units to show the Algebraically, these transformations correspond to adding or subtracting terms to the parent function and to multiplying by a constant For example, the function y = 2x^2 4x can be derived by taking the parent function y = x^2, multiplying it by the constant 2, and then adding the term 4x to it Read Also What Are Agents of Socialization?



Ex Determine The Equation Of A Transformation Of Y 2 X Youtube



2
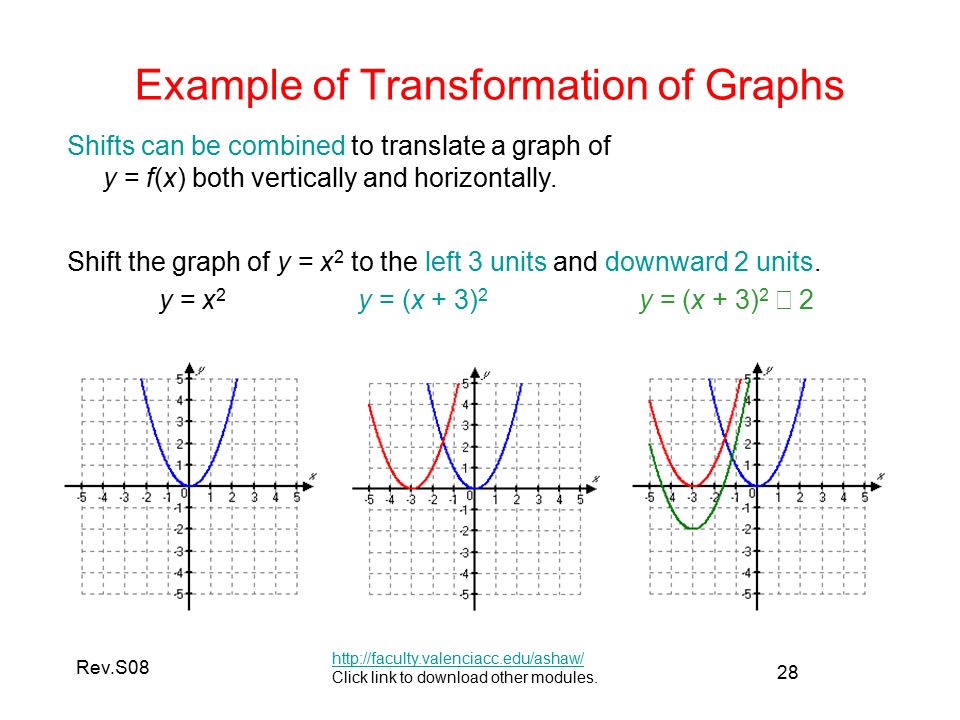
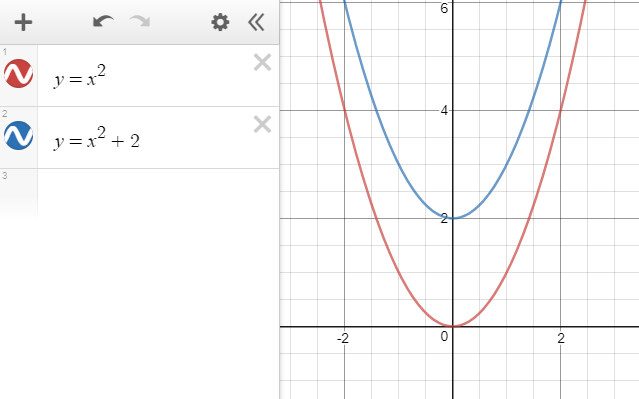
Example 2 y = x 2 − 2 The only difference with the first graph that I drew (y = x 2) and this one (y = x 2 − 2) is the "minus 2" The "minus 2" means that all the yvalues for the graph need to be moved down by 2 units So we just take our first curve and move it down 2 units Our new curve's vertex is at −2 on the yaxisShortcut Method for Finding the Standard Matrix Two examples 1 Let Tbe the linear transformation from above, ie, T(x 1;x 2;x 3) = 2x 1 x 2 x 3;180 seconds Q Which transformation maps the graph of f (x) = x 2 to the graph of g (x) = (x 4)2?




Apc Transformations Of Functions



Graphing Transformations Of Y X 2 Youtube
Transformations of Random Variables September, 09 We begin with a random variable Xand we want to start looking at the random variable Y = g(X) = g X where the function g R !R The inverse image of a set A, g 1(A) = fx2R;g(x) 2Ag In other words, x2g 1(A) if and only if g(x) 2A For example, if g(x) = x3, then g 1(1;8) = 1;2 About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsAs boundaries the curves x2 −y2 = 1, x2 −y2 = 4, y = 0, y = x/2 Solution Since the boundaries of the region are contour curves of x2 −y2 and y/x , and the integrand is y/x, this suggests making the change of variable (23) u = x 2 −y 2 , v = y x We will try to get through without solving these backwards for x, y in terms of u, v Since



Transformations Left Or Right




Transformation Of Graphs Highschool Learnmath
Dilation Dilation is also a transformation which causes the curve stretches (expands) or compresses (contracts) Multiplying a function by a positive constant vertically stretches or compresses its graph;Describe the Transformation y=x^2 y = x2 y = x 2 The parent function is the simplest form of the type of function given y = x2 y = x 2 For a better explanation, assume that y = x2 y = x 2 is f (x) = x2 f ( x) = x 2 and y = x2 y = x 2 is g(x) = x2 g ( x) = x 2 f (x) = x2 f ( x) = x 2 g(x) = x2 g ( x) = x 2Here we discuss transformations involving two random variable 1, 2 The bivariate transformation is 1= 1( 1, 2) 2= 2( 1, 2) Assuming that 1 and 2 are jointly continuous random variables, we will discuss the onetoone transformation first Starting with the joint distribution of




Sec 2 4 Transformation Of Graphs Copyright C By Houghton Mifflin Company Inc All Rights Reserved 2 The Graphs Of Many Functions Are Transformations Ppt Download




Function Transformations
TRANSFORMATIONS OF RANDOM VARIABLES 5 3 METHOD OF TRANSFORMATIONS(SINGLE VARIABLE) 31 Discrete examples of the method of transformations 311 Onetoone function Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads obtained in four tossesof a coin where the probability of a head is 060Function Transformations Just like Transformations in Geometry, we can move and resize the graphs of functions Let us start with a function, in this case it is f(x) = x 2, but it could be anything f(x) = x 2 Here are some simple things we can do to move or scale it on the graphWe are given the function y = x2 y = x 2 The graph of this function changes to y = −x2 y = − x 2 The graph transformation that happens in this function is Reflection over the xaxis
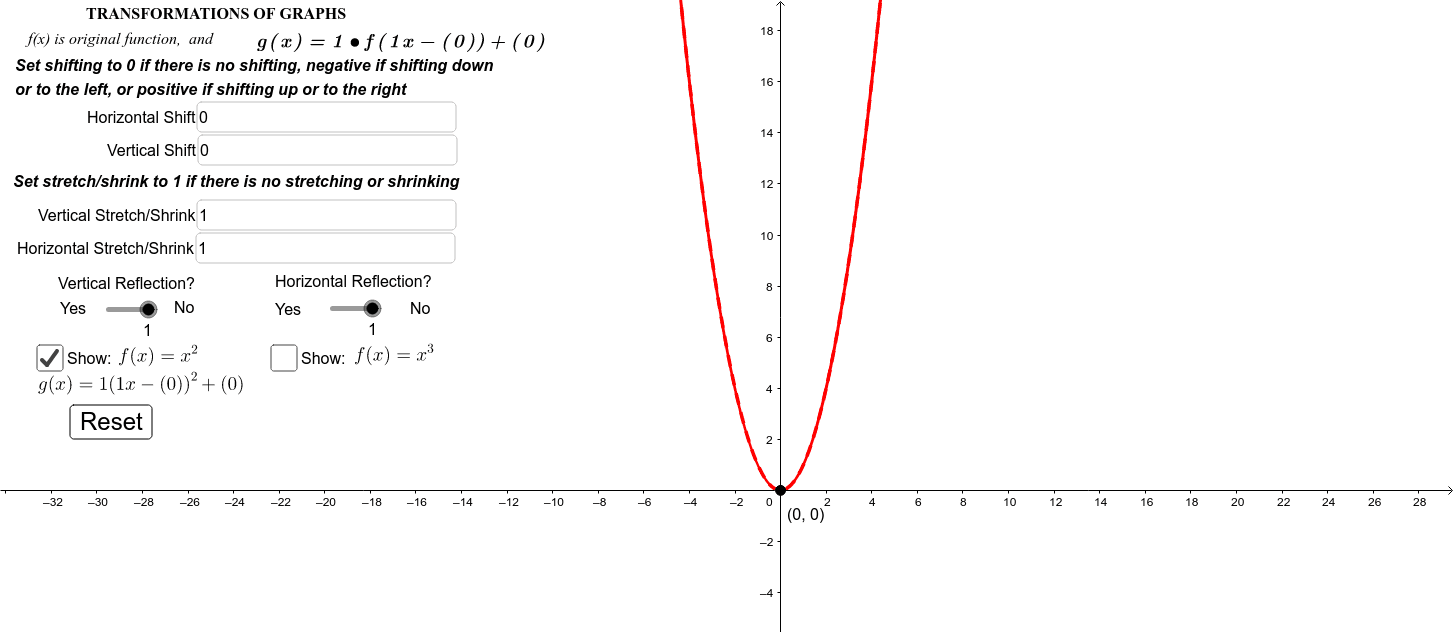



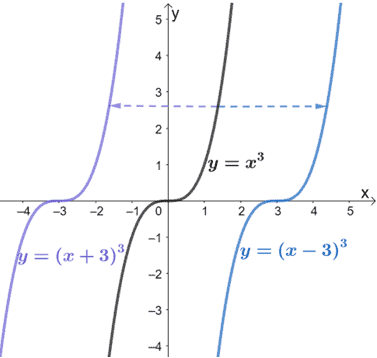
Transformation Of Y X 2 And Y X 3 Geogebra
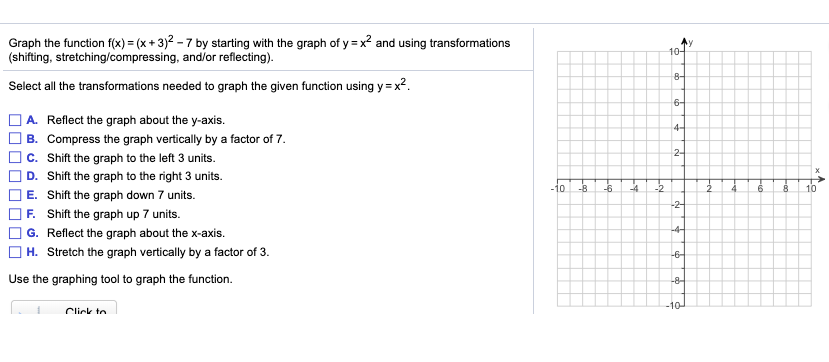



Graph The Function F X X 3 2 7 By Starting With Chegg Com
Transformations of Graphs Reflections We will discuss two types of reflections is a parabola shifted 9 units down with respect to the base function y = x 2 What do you suppose the graph of y 1 (x) = f (x) looks like?Now let us consider $Y = X^2$ This variable is clearly nonnegative and since $X$ is supported on $1,2$, we must have that $Y$ is supported on $0, \max((1)^2,2^2) = 0,4$ This is intuitively clear because the variable $X$ (with probability $1$) takes values in 1,2 and so $X^2$ takes values in $0,\max((1)^2,(2)^2)$Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more
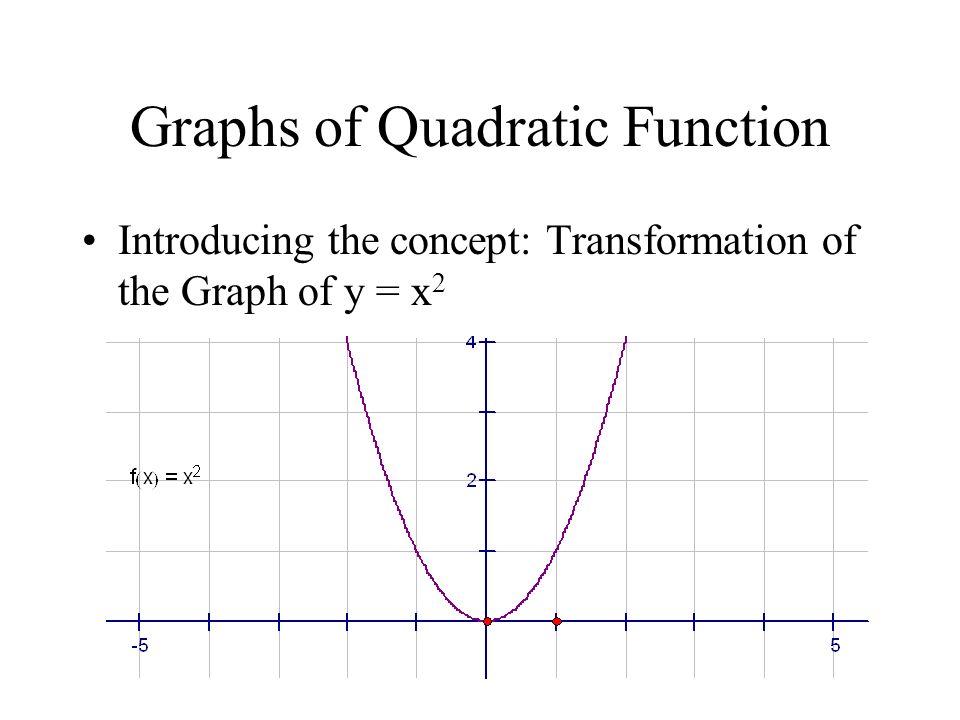



Graphs Of Quadratic Function Introducing The Concept Transformation Of The Graph Of Y X Ppt Download




Transformations For Each Slide Choose The Correct Answer From The List Of Choices Using The Mouse Cursor All Slide Transitions And Animations Use A Left Ppt Download
Now consider a transformation of X in the form Y = 2X2 X There are five possible outcomes for Y, ie, 0, 3, 10, 21, 36 Given that the function is onetoone, we can make up a table describing the probability distribution for Y TABLE 3 ProbabilityofaFunction oftheNumberofHeadsfromTossing aCoin Four Times Y = 2 * (# heads)2 # of headsSECTION 13 Transformations of Graphs MATH 1330 Precalculus 87 Looking for a Pattern – When Does the Order of Transformations Matter?The linear transformation rule (p, s) → (r, s) for reflecting a figure over the oblique line y = mx b where r and s are functions of p, q, b, and θ = Tan 1 (m) is shown below Finding the linear transformation rule given the equation of the line of reflection equation y = mx b involves using a calculator to find angle θ = Tan 1 (m



How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 2 And Describe The Transformation Socratic



Vce School Notes Graph Transformations
A nonrigid transformation A set of operations that change the size and/or shape of a graph in a coordinate plane changes the size and/or shape of the graph A vertical translation A rigid transformation that shifts a graph up or down is a rigid transformation that shifts a graph up or down relative to the original graph This occurs when a constant is added to any functionNote, again, that X = 0 has to transform into Y = 0 and hence minus is appropriate This gives the solution y(x) = 1− √ 4−x2 2 Transforming a Uniform Distribution It would be unusual to wish to transform a triangular distribution but there is a good reason for wanting to be able to transform a uniform distribution into something elseLine Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp Conic Sections Transformation Matrices & Vectors Matrices Vectors Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections y=x^{2} en Related Symbolab blog posts Functions A function basically relates an input to an output, there's an input, a relationship and an output For every input



How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 2 2 And Describe The Transformation Socratic



Transformation Of Graphs Ppt Video Online Download
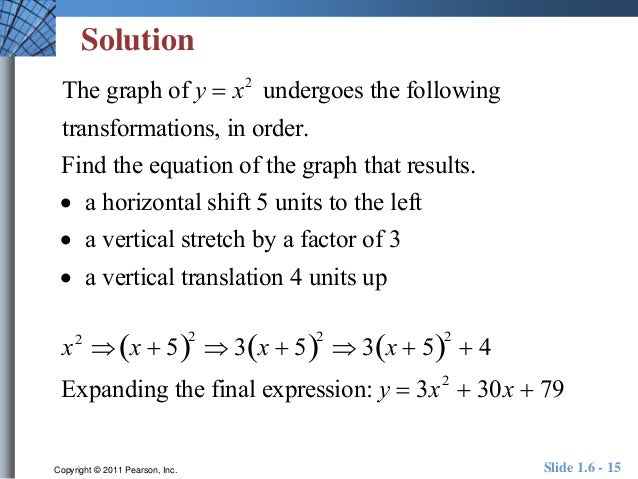
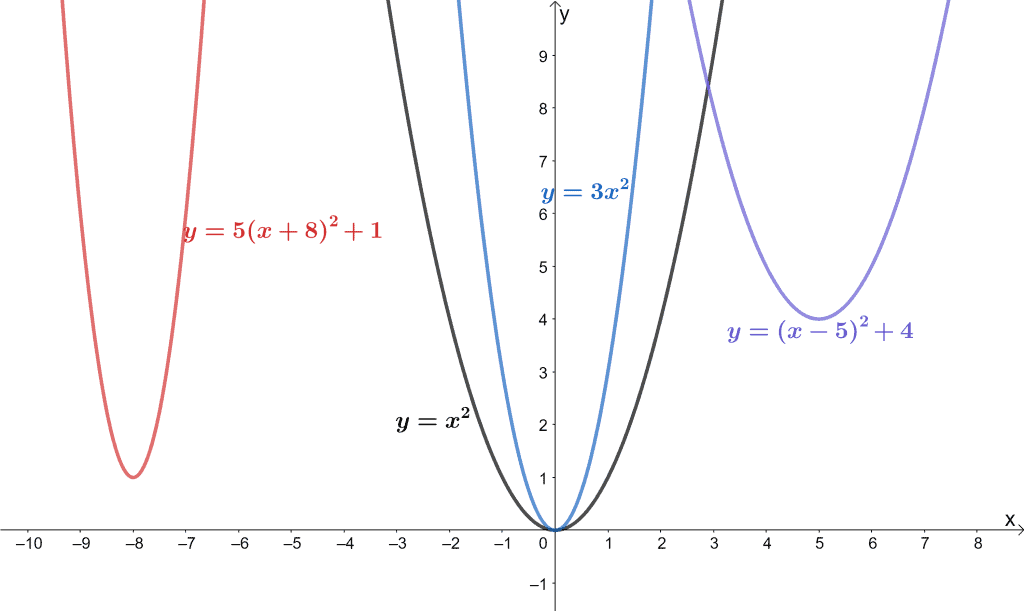
180 seconds Q Which transformation maps the graph of f (x) = x 2 to the graph of g (x) = (x 4)2?Applying transformations step by step 9 • The order in which transformations are applied will determine the "nal equation 1 Translation of 3 units to the right y=(x−3)2 4 Translation of 4 units up 2 Dilation by 2 from the x axis 3 Re!ection about xTranslations parallel to the yaxis If \ (f (x) = x^2\), then \ (f (x) a = x^2 a\) Here we are adding \ (a\) to the whole function The addition of the value \ (a\) represents a vertical



Transformations Of Y X2 In Vertex Form Organizer And Presentation




Grade 10 Transformations Of Y X 2 Youtube
Describe, using appropriate terminology, the transformations that occurred to y=x^2 in order to become y=2(x3)^25 First there is a vertical reflection because of the in front of the 2 Second there is a horizontal translation right 3 because of the 3Answer choices a reflection across the line x = 4 a reflection across the line y = 4 a translation shifting f (x) 4 units to the left a translation shifting f (x) 4 units to the rightX 1 3x 2 2x 3;3x 2 4x 3 Then the rst, second and third components of the resulting vector w, can be written respectively



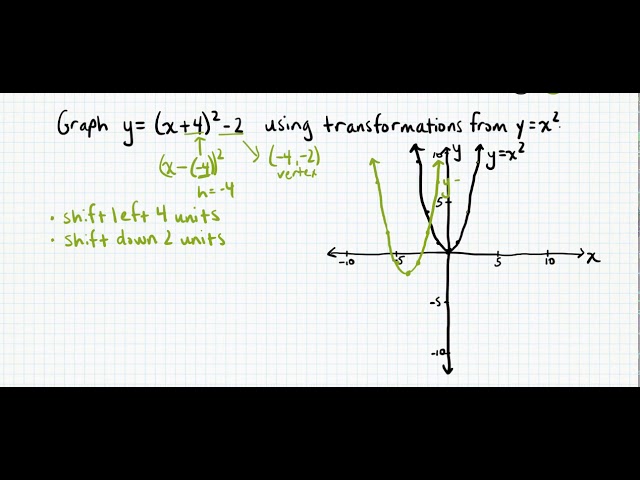
Solution I Have A Question That States A Use The Transformations On The Graph Of Y X 2 To Determine The Graph Of Y X 5 2 9 B Using The Graph Of F X X 2 As A Guide Graph



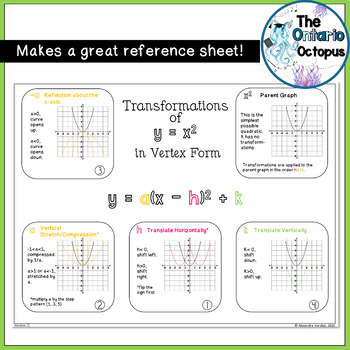
Trasformations By Graph Paper Teacher Guide
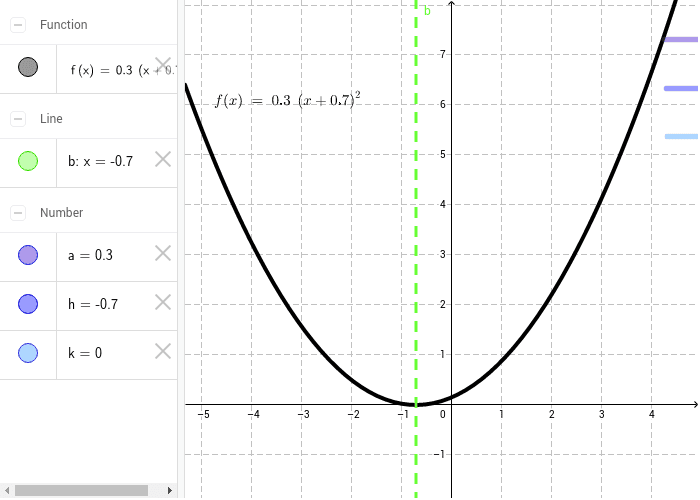
Is it a)horizontal translation of 4,vertical translation of 3,stretch of 5, reflection in xaxis b) ht of 4,vt of 3, stretch of 5, reflection in xaxisIdentify the vertex and axis of symmetry for a given quadratic function in vertex form The standard form of a quadratic function presents the function in the form f (x)= a(x−h)2 k f ( x) = a ( x − h) 2 k where (h, k) ( h, k) is the vertex Because the vertex appears in the standard form of the quadratic function, this form is alsoY=X^2 Transformations Y=X^2 Transformations Log InorSign Up y = a bx − h 2 k 1 h = 0 2 k = 0 3 a = 1 4 b =




How To Graph Transformations Of Functions 14 Steps
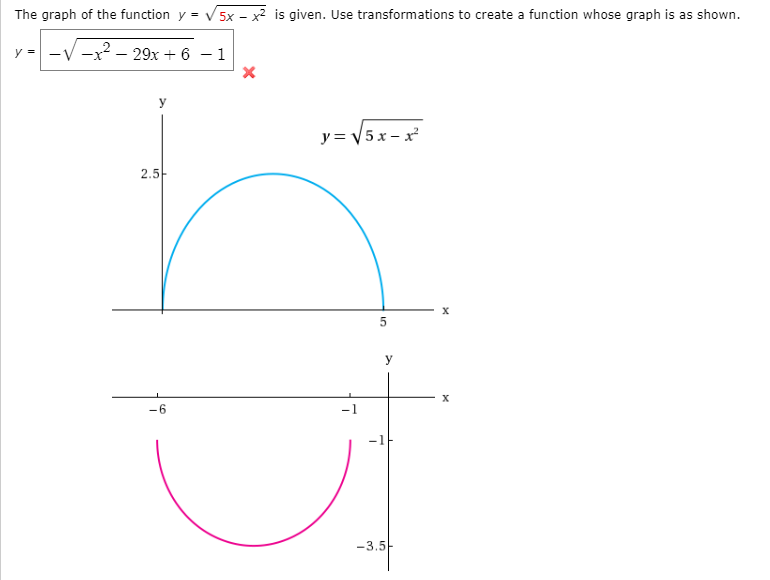



Answered The Graph Of The Function Y V 5x X Bartleby
For example, if you know that the quadratic parent function \(y={{x}^{2}}\) is being transformed 2 units to the right, and 1 unit down (only a shift, not a stretch or a flip), we can create the original tchart, following by the transformation points on the outside of the original points Then we can plot the "outside" (new) points to getThe transformation is T ( x1,x2) = x1x2, 3x1 So if we just took the transformation of a then it would be T (a) = a1a2, 3a1 a1=x1, a2=x2 In that part of the video he is taking the transformation of both vectors a and b and then adding them So it is x1 = a1, b1 To determine which transformations we need to apply to the graph of \(f\) to obtain the graph of \(j\), we rewrite \(j(x) = \sqrt{x3} = f(x3)\) Comparing this formula with \(f(x) = \sqrt{x}\), we see that not only are we multiplying the input \(x\) by \(1\), which results in a reflection across the \(y\)axis, but also we are adding \(3\), which indicates a horizontal shift to



1
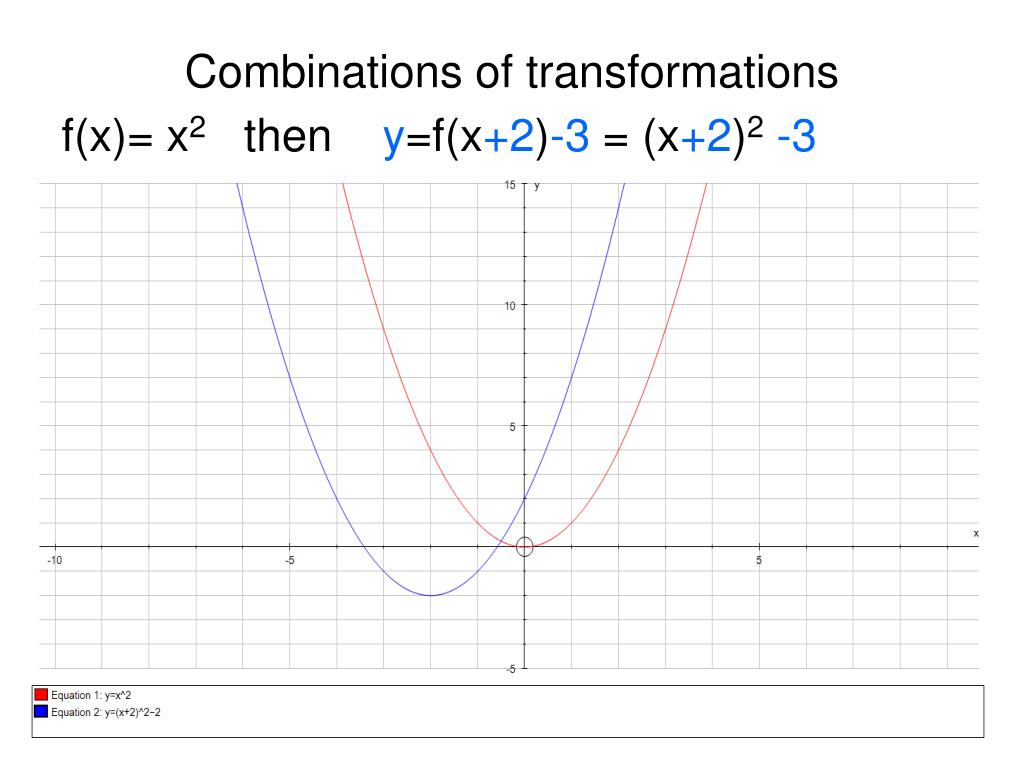



Ppt Transformation Of Graphs Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
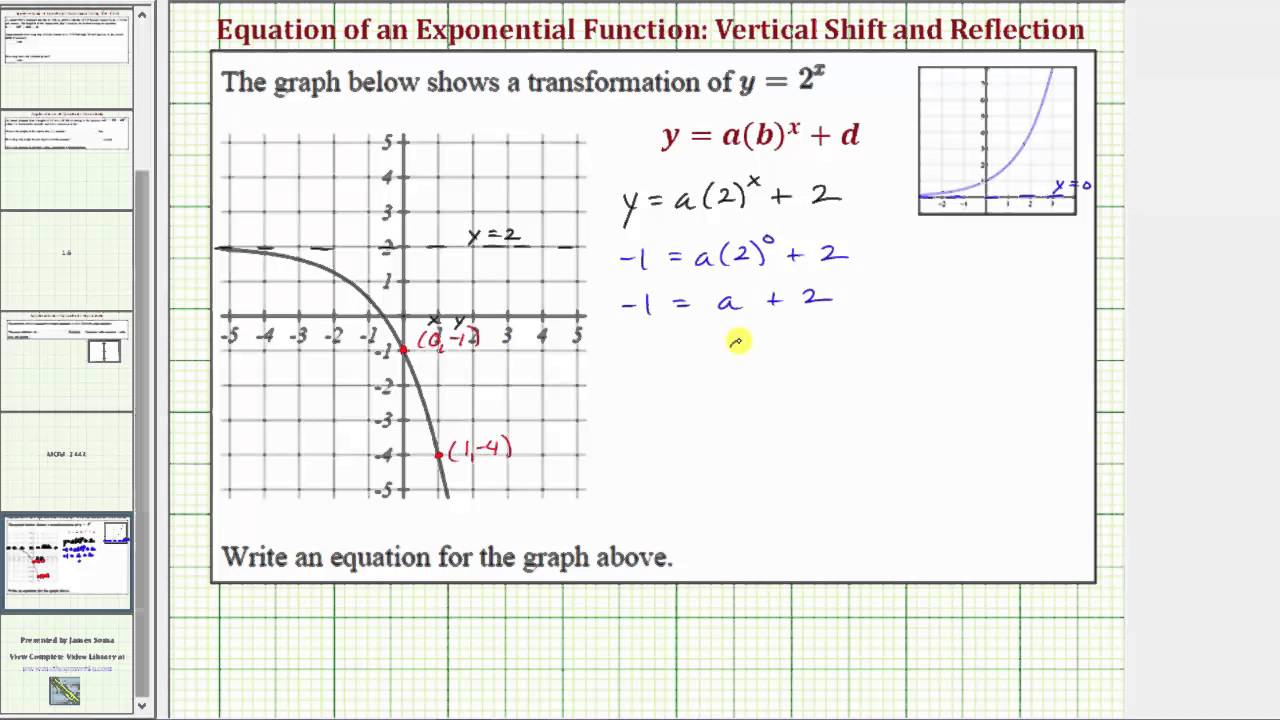
Question What Transformation of y=2^x results in the equation 1/5(y3)=2^(x4)?
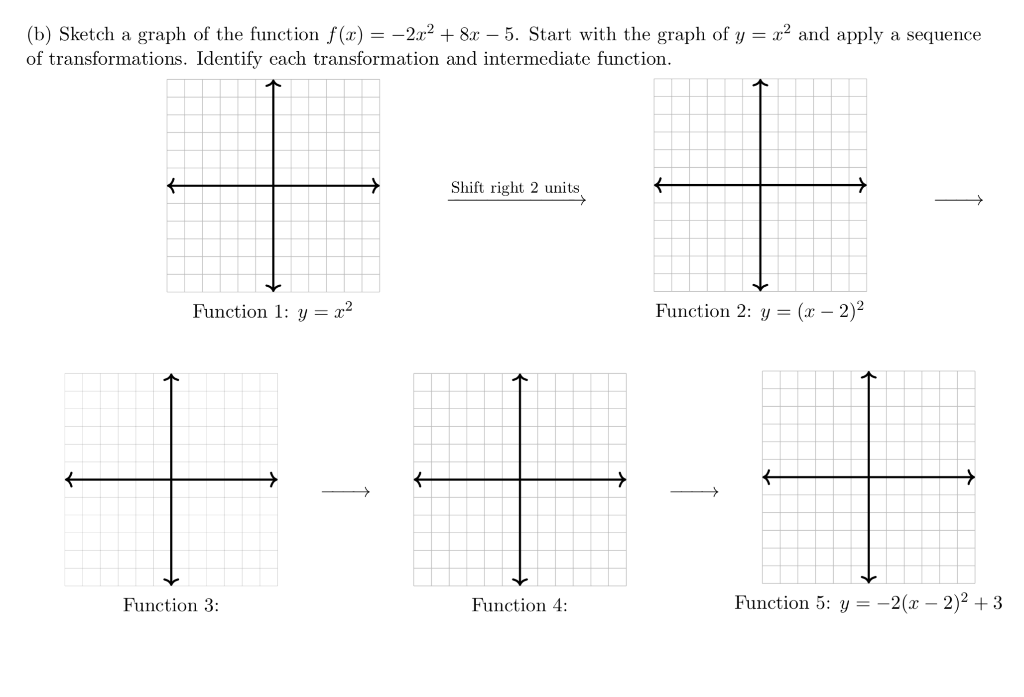



B Sketch A Graph Of The Function F X 2 R2 8x Chegg Com




Parabola Party Hosted By Quadratic Functions All Others



Solved Match The Rule With The Transformation Y X 2 X Y 3 Y X 4 X Y 5 X 3 Y 5 6 Y X 7 X Y 8 Y X 9 Course Hero
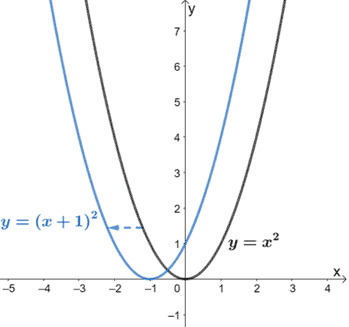



Transformations Of Functions Explanation Examples




Vertical And Horizontal Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation




The Transformation Of The Graph Of A Quadratic Equation Matherudition




Pin On High School Mathematics Classroom Ideas



Transformations To The Graph Of Y X 2 Geogebra




Content Transformations Of The Parabola




Transformation Of Graphs Asymptote Cartesian Coordinate System




Describe How The Graph Of Y X 2 Can Be Transformed Chegg Com



Quadratic Transformations Part 2 Activity Builder By Desmos




Unit 1 6



2



2



Desmos 2 Transformations Of Graphs Cambridge Maths Hub



Transformations Of Functions Explanation Examples



Discovering Advanced Algebra Resources



Parent Function Worksheet 2



Transforming Graphs Of Functions Brilliant Math Science Wiki



Using Transformations To Graph Functions Of The Form



3



Parabola Transformations Zona Land Education



Absolute Value Transformations




Stretching And Reflecting Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation



Exploring Transformations Of Parent Functions



Transformations Bingo Card
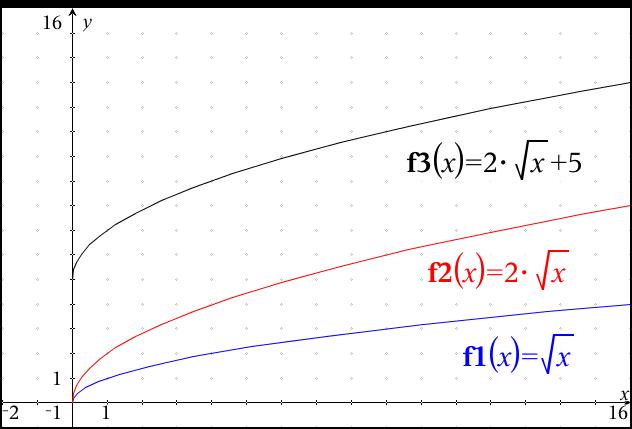



How Do You Identify Transformations In Parent Functions Given Y 2sqrtx 5 Socratic



Transformations Mrs F X
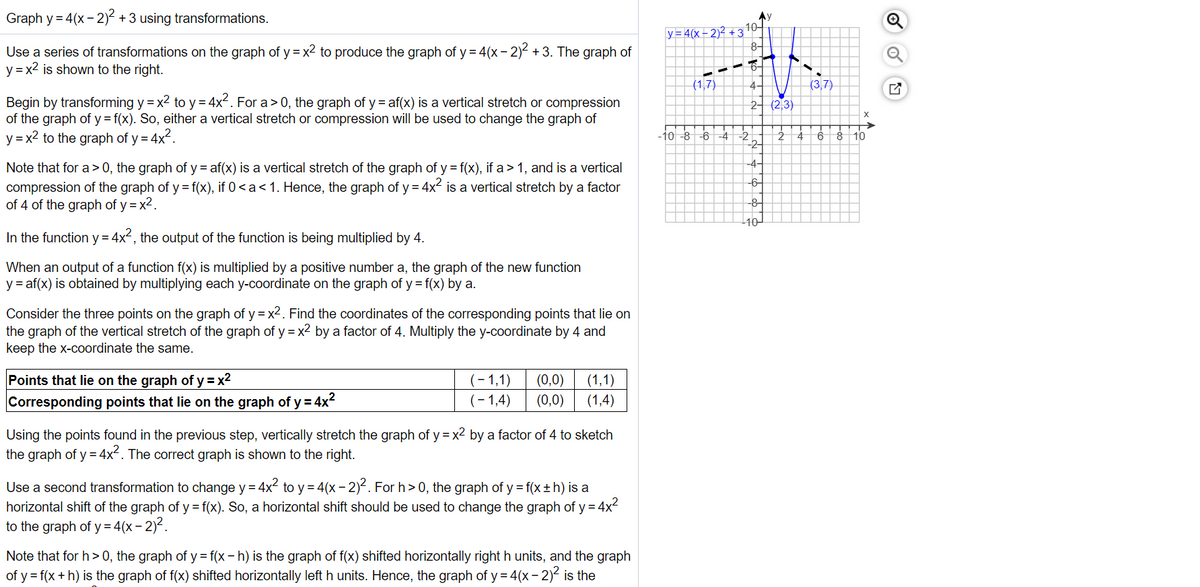



Answered Graph Y 4 X 2 3 Using Bartleby




Transformations Of Quadratic Functions The Translations Dilations And Reflections




1 07 Transformations Of Functions




Chapter 2 Functions And Graphs Section 2 Elementary Functions Graphs And Transformations Ppt Download




Sketch The Graph Of The Equation Y X 2 2 3 Study Com
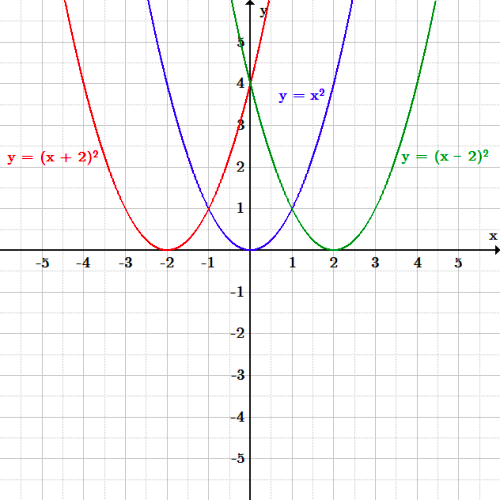



Transformations Boundless Algebra
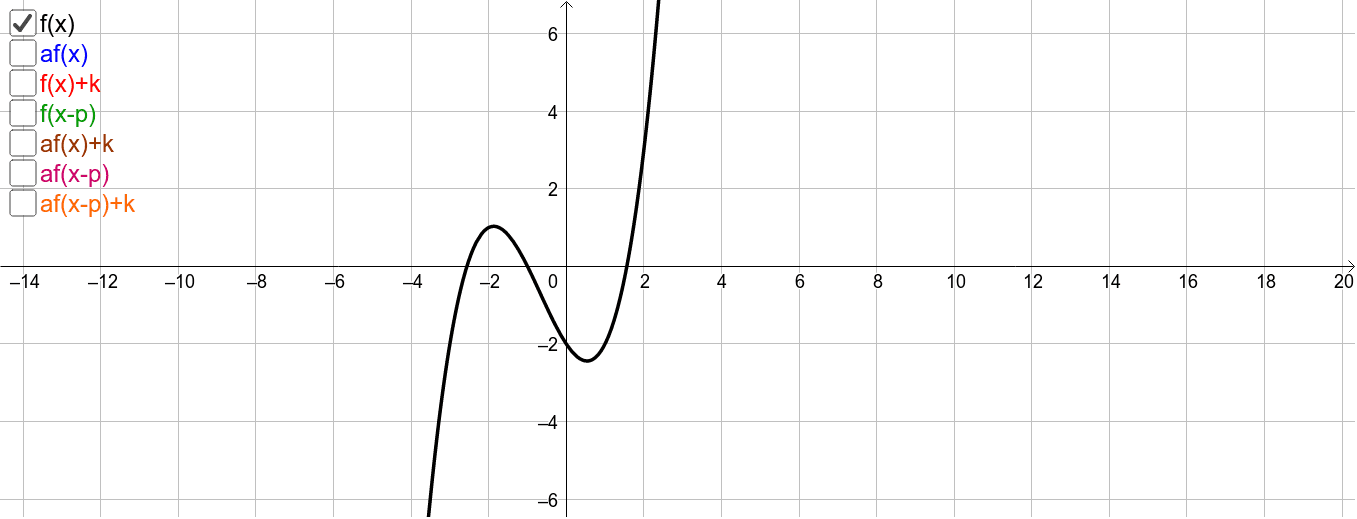



Y X 2 Transformation Geogebra
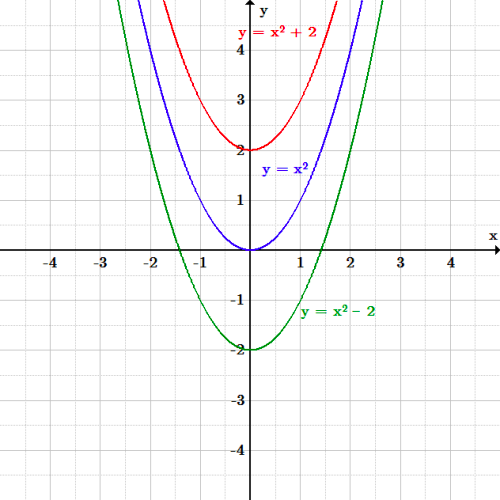



Transformations Boundless Algebra




Investigate The Effects Of Various Transformations On The Given Right Triangle Use The Coordinate Notation To Help You Find The Image Of Each Vertex Of The Triangle Plot The Images Of The



2




The Graph Of The Function Y Sqrt 3x X 2 Is Given Use Transformations To Create A Function Whose Graph Is As Shown Study Com
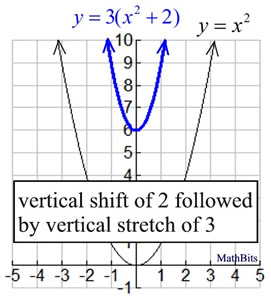



Sequence Of Transformations On Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math



1
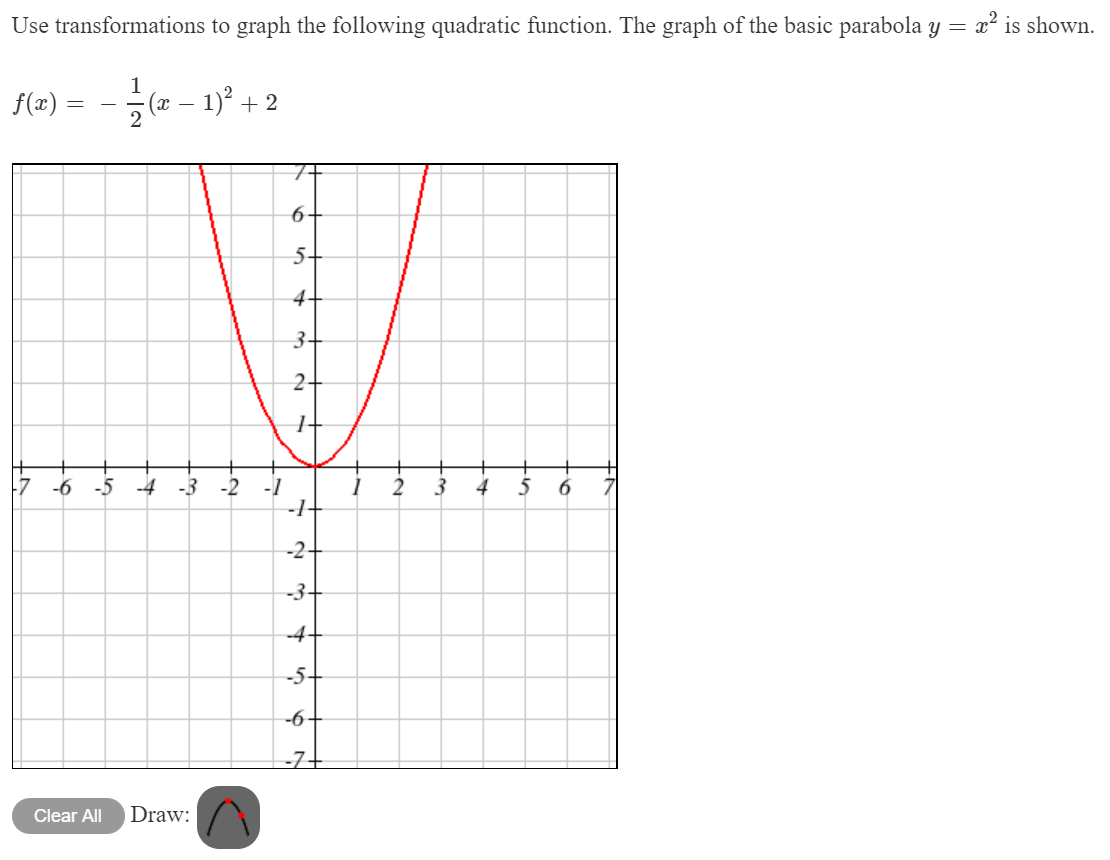



Use Transformations To Graph The Following Quadratic Chegg Com
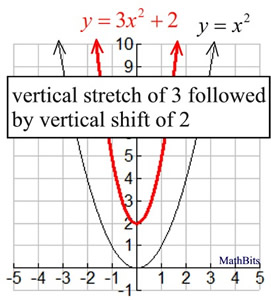



Sequence Of Transformations On Functions Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math




Symmetry Transformations And Compositions



3 5 Transformations Of Functions 2 5 Ncb 502 Corequisite For Mat 1023 Openstax Cnx



Horizontal And Vertical Graph Stretches And Compressions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions




Combining Transformations Read Algebra Ck 12 Foundation




Content Geometric Transformations Of Graphs Of Functions
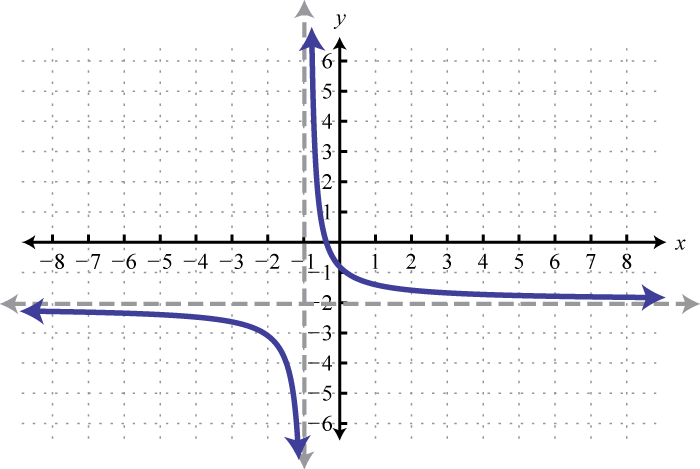



Using Transformations To Graph Functions




Content Transformations Of The Parabola




Transformations In Math Definition Graph Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Search Q Parabola Equation Tbm Isch
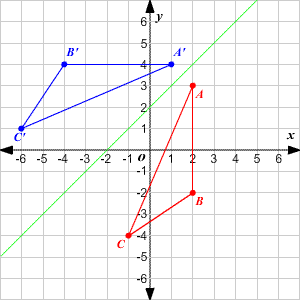



Transformations Of Graphs
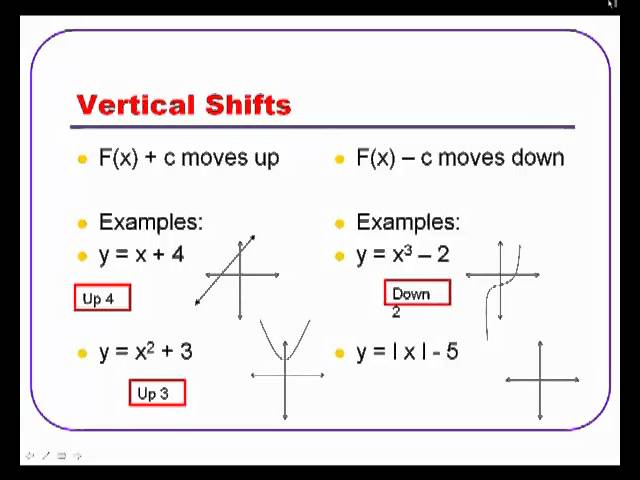



Algebra 2 Transformations Of Parent Functions Youtube




Solution Order Order Combining Functions Underground Mathematics




Transformations Of Y X Ck 12 Foundation
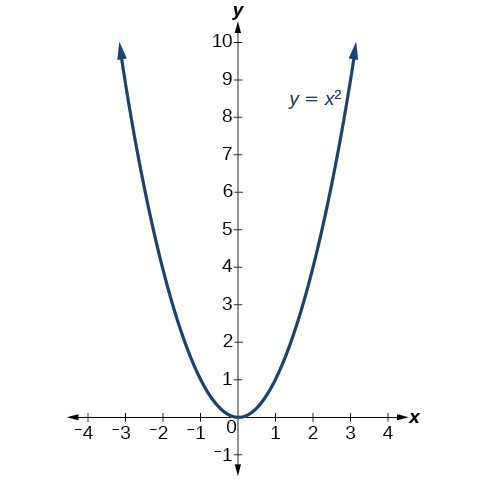



Transformations Of Quadratic Functions College Algebra



Jdlogo Home Functions Defined Functions You Should Know Transformations Of Quadratics Translations Reflections Inverses Stretches Combinations Combining Functions Review Test Unit 2 Functions And Transformations Lesson 3a
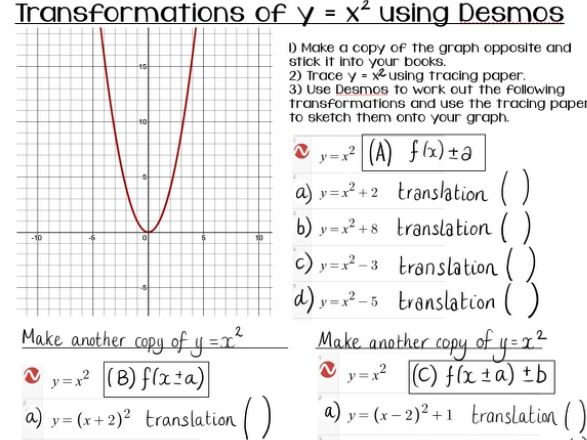



Transformations Of Y X 2 Using Desmos Teaching Resources




Transformations




Which Sequence Of Transformations Produces A Congruent Figure Note Each Answer Choice Represents A Brainly Com




Using Transformations To Graph Functions
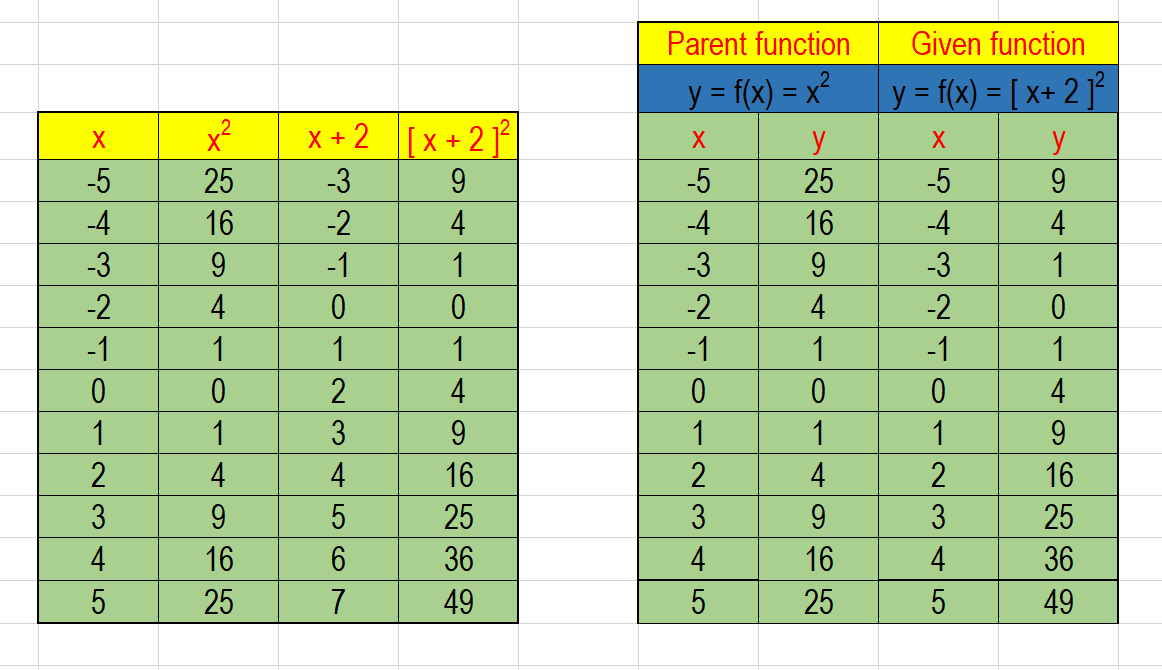



How Do You Sketch The Graph Of Y X 2 2 And Describe The Transformation Socratic
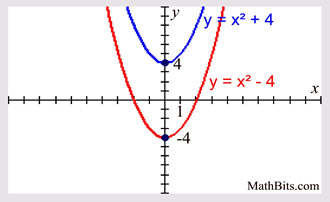



Parabola Parent Function Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math



2




Which Type Of Transformation Is Described By X Y X 2 Y 3 Brainly Com



View Question 1 Describe The Transformation Done To The Parent Function Y 2x In Each Equation Below
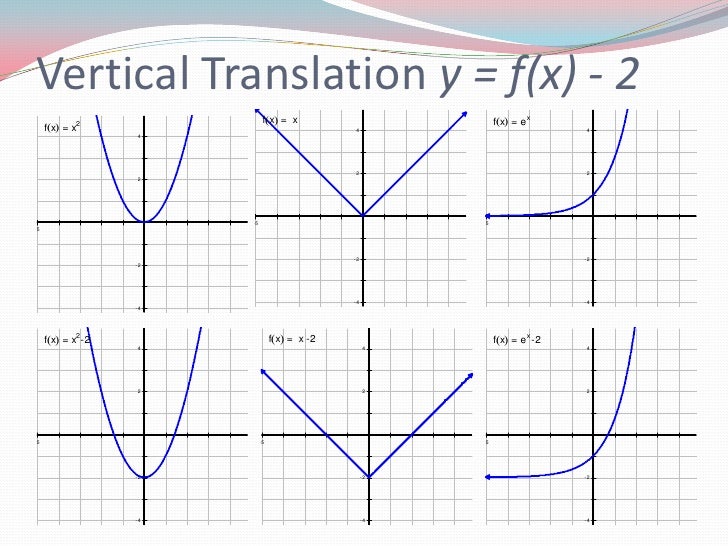



Transformations




Function Transformations



2




1 7 Transformations Mathematics Libretexts
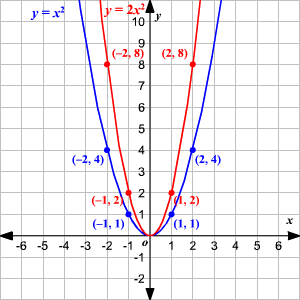



Graphing Quadratic Equations Using Transformations




Transformations Of Functions Ck 12 Foundation



Biomath Transformation Of Graphs
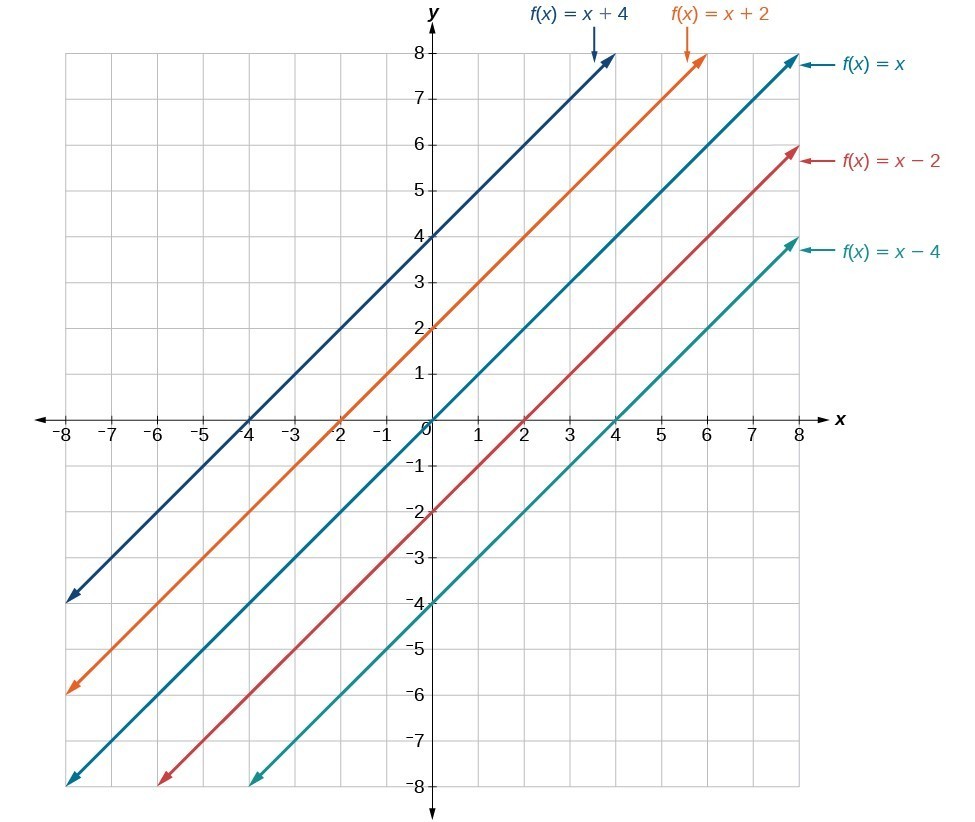



Read Transform Linear Functions Intermediate Algebra



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿